A Crash Course on Climate Change
Climate change
Climate change
Climate is a “complex” system
Lorenz attractor: introduction to chaos
Greenhouse effect
A timeline of climate
Topics discussed
How climate works (simple version)
Can we trust climatologists and climate science?
Anthropogenic CO2 emissions
Foreseeable consequences of CO2 accumulation : damages
From where whom ? heterogeneity of CO2 emissions, inequelaties and differenciated responsabilities
What can we do about it? mitigation and geoengineering
Climate is a “complex” system
Climate change
Climate is a “complex” system
Lorenz attractor: introduction to chaos
Greenhouse effect
A timeline of climate
Climate is a complex system
Matter, heat, chemical and biological transformations flows between lithosphere, atmosphere (stratosphere, troposphere), hydrosphere, biosphere
Intertwining of dynamics of different timescale : from 1b years processes to a few hours time constant (fast/slow dynamics, a gigantic chaotic wheel)
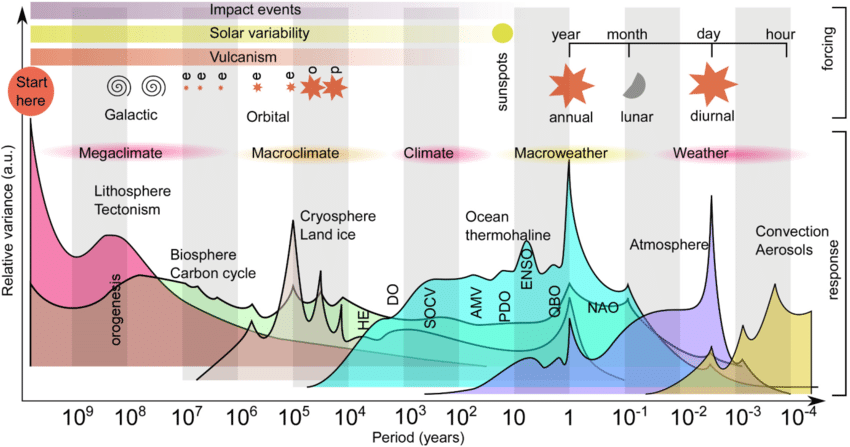
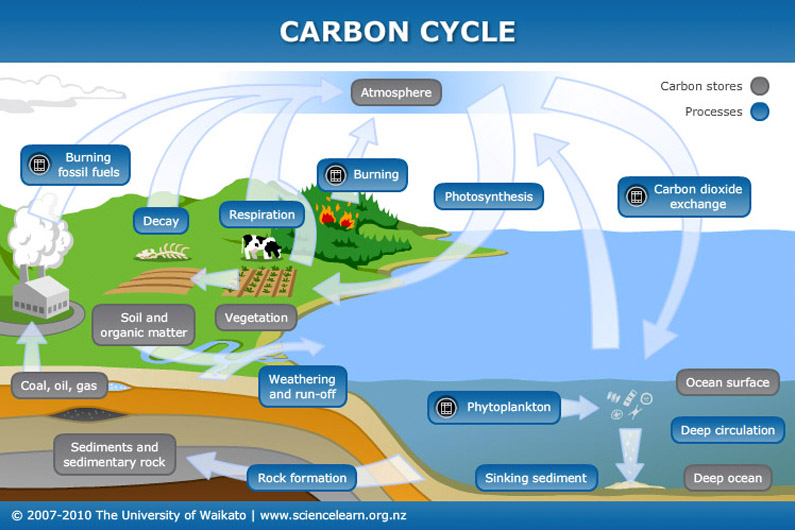
Why CO2 matters so much ?
CO2 matters because it has a very complex cycle, implied in
Bioprocesses (carbon is the building brick for most know life),
Energy storage and release (partially related to previous point)
Sedimentation and volcanic activity
Changes in atmospheric CO2 concentration are larger and more persistent (100+y)
Water has a much simpler cycle than CO2
Although GH power of water is higher;
A lot of incident energy is provided by the Sun
The climate system uses this energy, to make climate going as well as life
Life and climate are closely interconnected
Lorenz attractor: introduction to chaos
Climate change
Climate is a “complex” system
Lorenz attractor: introduction to chaos
Greenhouse effect
A timeline of climate
Chaotic Wheel
The butterfly effect
Designed and formalized in the 1960’s by Willem Malkus at MIT as an illustration of the Lorenz paper on heat equations (plus a mechanical device)
The butterfly picture is in the plan [position/speed]
The wheel is mathematically related to Lorenz equations of heat in atmosphere
Movement of wheel is chaotic but a pattern emerge despite sensitivity to initial conditions (butterfly effect)
- Butterfly effect is detrministic, but not causal, it is chaotic
Greenhouse effect
Climate change
Climate is a “complex” system
Lorenz attractor: introduction to chaos
Greenhouse effect
A timeline of climate
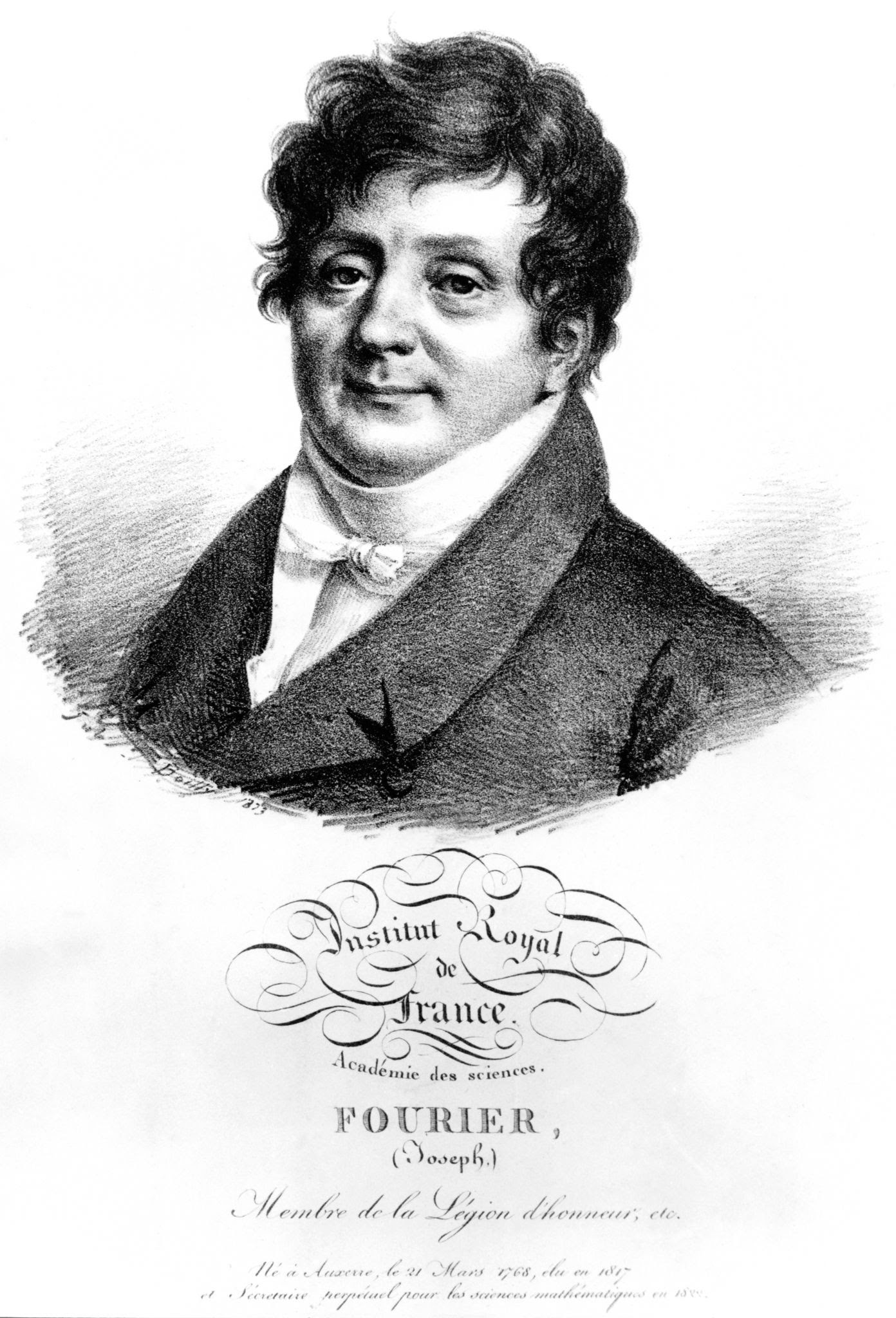
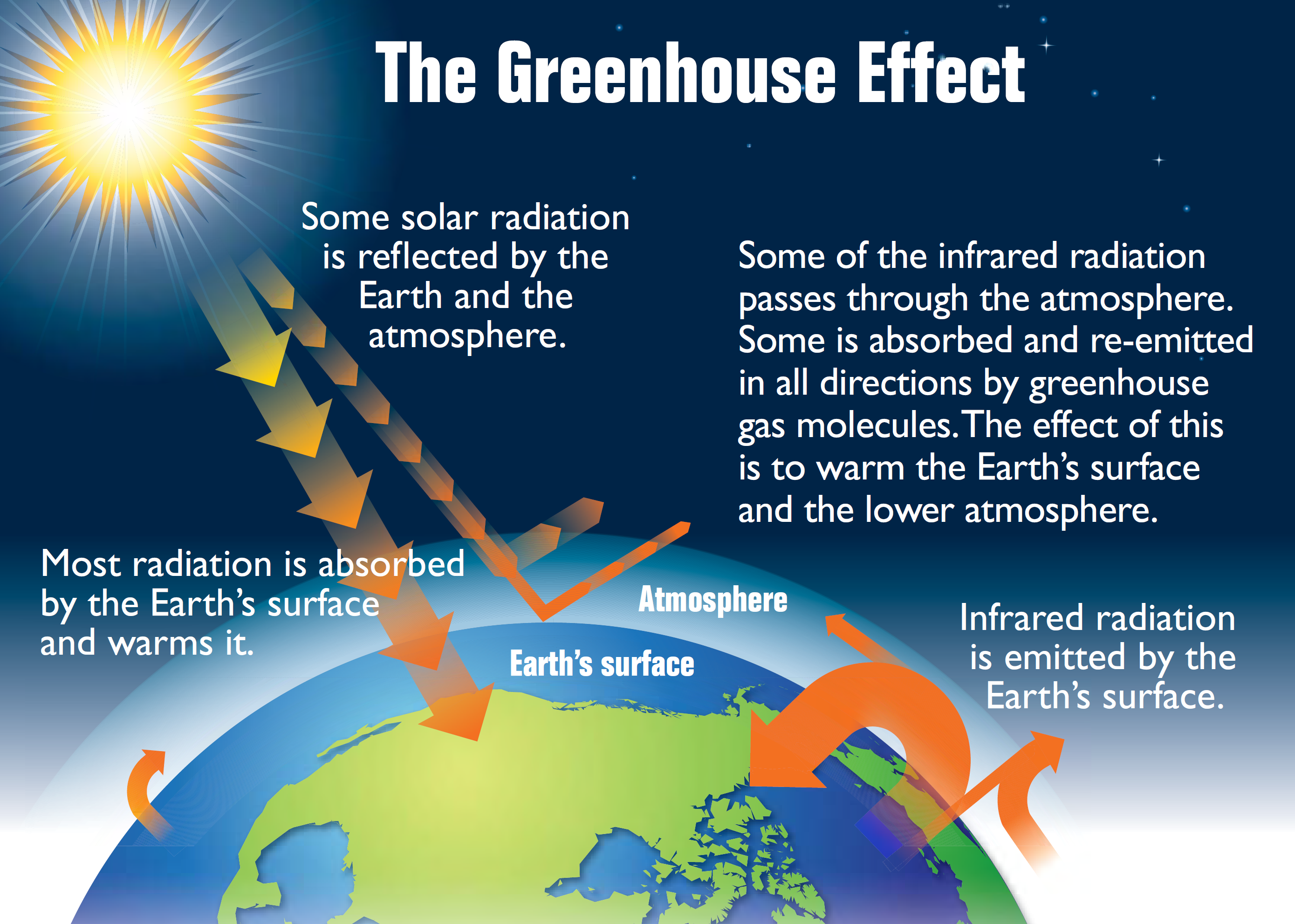
Green House Effect is necessary to understand earth temperature and climate
Joseph Fourier (1823) established that earth temperature should be -18°Celsius by calculating heat balance of earth system (radiation of the black body in the void)
- Something has to be added, he proposed “ether” with a non-zero temperature (note 0°K or absolute 0 is -273°C)
GHG and effect were discovered by Lyndall
- Light and other radiation from Sun carry energy, part of it is reflected (atmosphere, clouds, albedo), part of it is absorbed by the ground.
- This heat is re-emited in a different radiation (Infrared) and then captured by GHG, transparent to light radiations but absorbing infrared.
Arrhenius calculated that a doubling of CO2 in atmosphere would increase temperature by 4°C
- He produced this estimation in 1896
- He thought that it was a way out of Little Ice Age

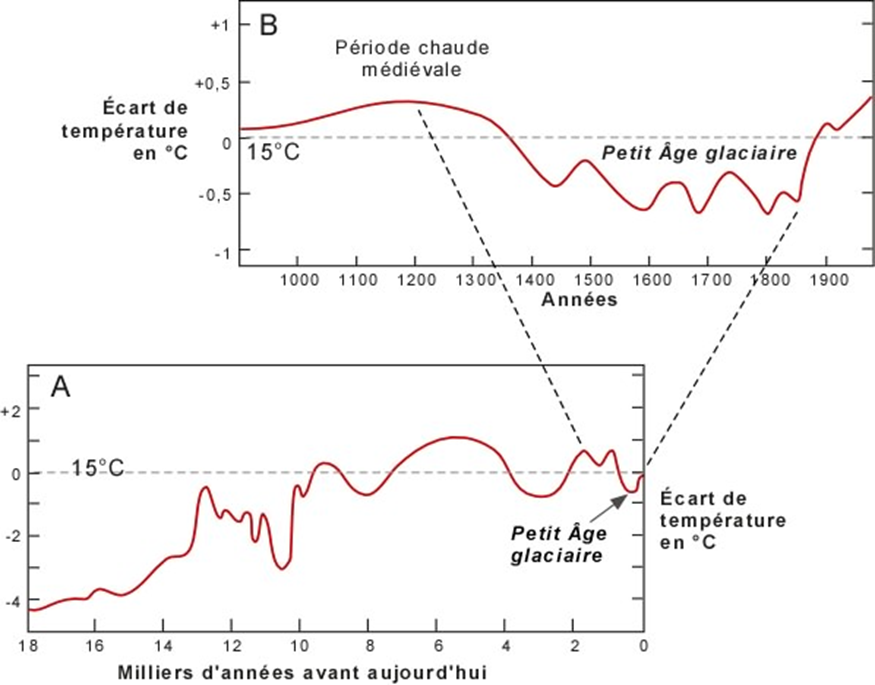
A timeline of climate
Climate change
Climate is a “complex” system
Lorenz attractor: introduction to chaos
Greenhouse effect
A timeline of climate
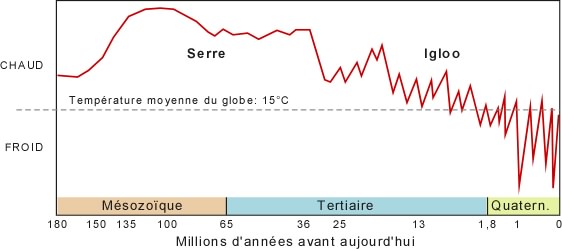
Climate has been stable… for a long time
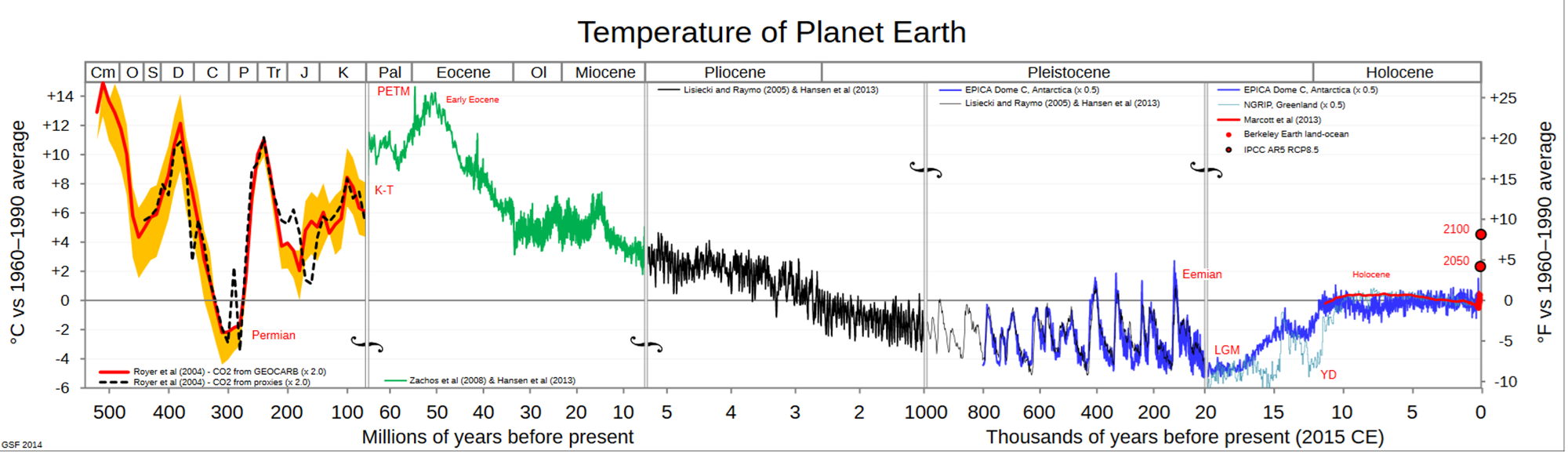
Civilization and climate
- Relatively cold and stable since a few million years
- Quaternarian Ice ages, the last one ended 10k before us
- Very stable since a few 100k years
- 8 to 10 °Celsius range
- Mamal best life period
- Strong biodiversity impact of change in temperature
- Climate has been very stable since 10k
- Civilization time frame
- Bioselection by human,
- Colonization of the whole planet by humans
- However, There is no causal (scientifically demonstrated) link between climate and civilization
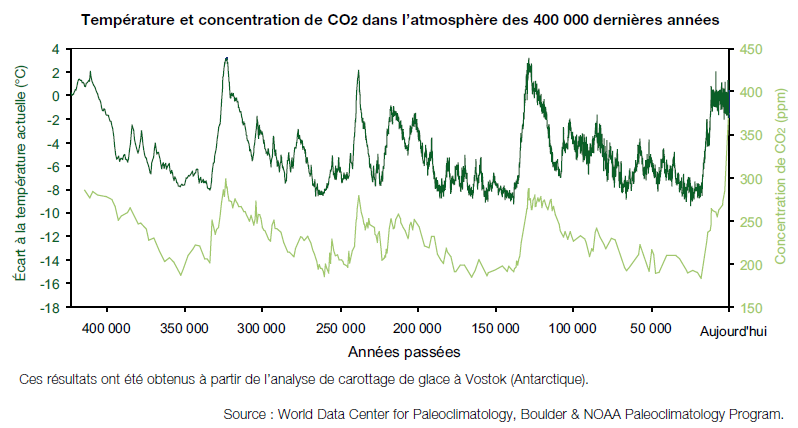
Climate and CO2 concentration are linked
Many feedback loops, positive or negative
- The more CO2, the warmer the Earth (more GH effect) (positive)
- The warmer the earth, the more heat is transported all around (more energy means more movment) (positive or negative)
- The more CO2 the more oceans absorb CO2 (the more acid they are) (positive)
- The warmer earth is, the less oceans absorb CO2 (positive)
- The warmer the earth is, the less aldedo reflects incoming heat (ice caps melting) (positive)
- The warmer earth is, the more vegetation (or plancton) is active, the more CO2 is absorbed by biosphere (negative)
- The more acid are the oceans, the less plancton (given dominant in current pH condition species) (negative)
- More CO2 means more vegetation, but means also different vegetation, younger one (positive)
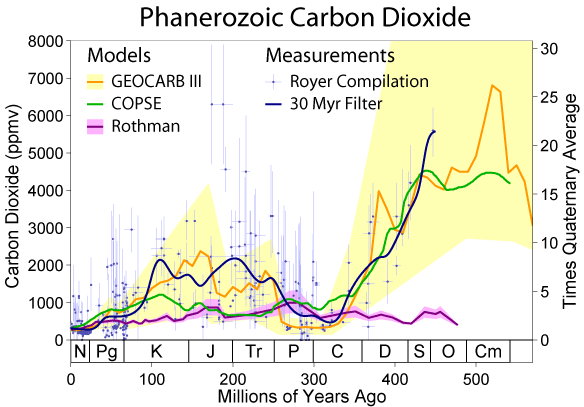
Impact on long term storage of carbon is ambiguous and complex
Speed of change is important
- Biosphere can adapt differently to fast changing conditions
- In the past : change in CO2 have been triggered by change in temperature
- Most probable explanation : Milankovic cycles (e, o, p changes)
- Change in temperature are then amplified by change in CO2 (through GHE)
climate change had an impact on civilization
Stabilisation of climate and civilization
Ruddiman hypothesis early anthreopocen, deforestation increases CO2 and may be some other GHG
The peak of the Roman Empire was a warm period
Dark ages were a cold period
Little Ice Age
The French Revolution is linked to bad weather and crops (due to cold and rainy summers)
A change ?

Art commentary quiz!

A few degrees matters!

A few degrees matters : Consequences

A Crash Course on Climate Change EoE 2026: The Age of Constraints